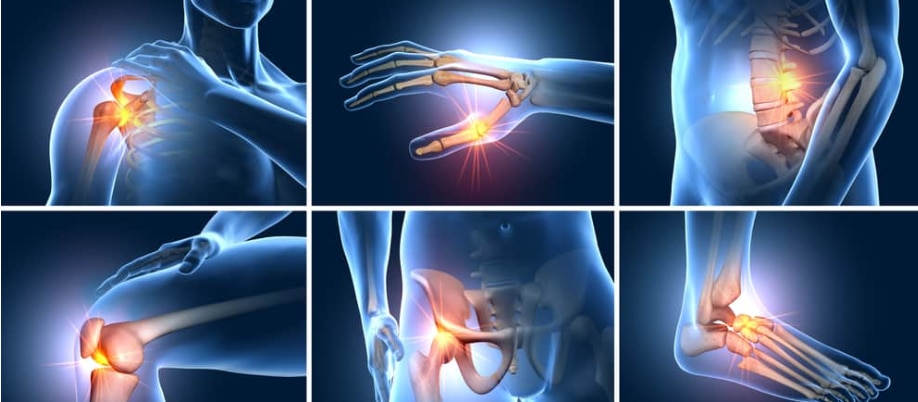
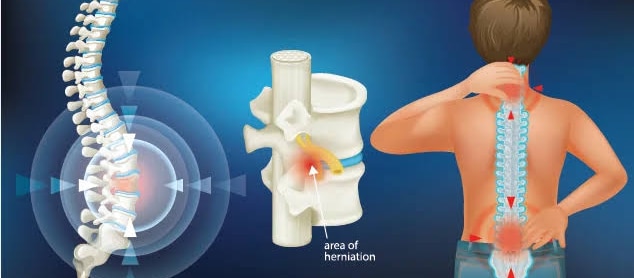
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the treatment and rehabilitation of ligament injuries, aiming to reduce pain, restore range of motion, improve strength and stability, and facilitate a safe return to activity. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual and the severity of the injury, often involving a combination of pain management techniques, exercise therapy, manual therapy, and proprioceptive training. Key Aspects of Physiotherapy for Ligament Injuries: Pain Management:Physiotherapists use various methods to reduce pain and inflammation, such as ice, heat, electrotherapy, and manual therapy. Restoring Range of Motion:Gentle exercises and joint mobilization techniques are used to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness. Strengthening Exercises:Progressive exercises, including isometric and dynamic movements, are designed to build strength in the muscles surrounding the injured ligament. Balance and Proprioception Training:Exercises to improve the body's awareness of joint position and movement are crucial for stability and preventing re-injury. Functional and Sport-Specific Training:Exercises that mimic daily activities or sports movements are incorporated to prepare the individual for a safe return to their desired level of activity. Bracing and Support:Depending on the severity and location of the injury, a brace may be used to provide support and stability during the healing process. Education:Physiotherapists provide guidance on activity modification, proper movement patterns, and strategies for preventing future injuries. Examples of specific treatments and exercises:Knee Ligament Injuries:Rehabilitation may involve exercises like quad sets, hamstring curls, leg extensions, and single-leg balance exercises. Ankle Ligament Injuries:Physiotherapy may include exercises like ankle pumps, alphabet tracing, and balance board exercises. Shoulder Ligament Injuries:Exercises may focus on rotator cuff strengthening, scapular stabilization, and range of motion exercises. Importance of Physiotherapy:Reduces Pain and Swelling:Physiotherapy helps manage pain and inflammation associated with ligament injuries. Improves Range of Motion and Flexibility:Exercises and manual therapy techniques restore joint movement and flexibility. Strengthens Muscles and Stabilizes Joints:Targeted exercises build muscle strength and improve joint stability, reducing the risk of re-injury. Enhances Proprioception and Balance:Proprioceptive training improves the body's awareness of joint position and movement, enhancing balance and coordination. Facilitates Return to Activity:Physiotherapy helps individuals safely return to their desired level of activity, whether it's daily tasks, sports, or work. Prevents Future Injuries:By addressing biomechanical issues and providing education on proper movement patterns, physiotherapy helps prevent future ligament injuries.
READ MORE